티스토리 뷰
1월 13일에 Notion에 정리했던 내용을 옮겨 적은 것입니다.
잘못된 내용은 댓글 부탁드립니다.
한동안 회사 일로 공부한 걸 게시할 시간이 없네요.. ㅠ
CGI? (Common Gateway Interface)
- HTTP 프로토콜 기반의 웹 서버와 다양한 언어로 구현된 프로그램 간의 데이터를 교환하는 표준 스펙이자 Interface이다.
- 일종의 Interface, 스펙이기 때문에 여러 언어로 구현이 가능하다

장점
- 여러 작업에 대한 많은 템플릿 코드들이 많이 존재한다.
- 표준 스펙을 준수하는 한 모든 언어와 플랫폼에서 작성될 수 있다.
단점
- 매 요청이 들어올 때마다 프로세스가 생성되고 각각의 CGI 구현체를 통해 동작한다.
- 메모리를 공유하는 쓰레드에 비해서 프로세스는 각자의 공간을 지니기 때문에 상대적으로 무겁고 생성되는데 시간이 상대적으로 오래 걸린다.
- 상대적으로 많은 처리 시간을 소모한다.

기존 방식의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 요청마다 스레드를 생성하게끔 변경하였지만, 결국 CGI 구현체가 계속해서 생성되는 것을 개선하지 못하였다.
Servlet

이전에 사용되던 기술인 CGI의 여러 문제점을 해결하기 위해 등장하였다.
- 웹 애플리케이션을 개발하기 위한 표준 스펙이자 Interface이다.
- 서블릿도 CGI 규약을 따르지만 이를 Servlet Container에게 위임하였고 Container와 Servlet 간의 규칙이 존재한다.
- Servlet 인스턴스는 Servlet Container를 통해 등록되고 Cycle이 관리된다.
- Servlet은 모든 요청을 받을 수 있으며, 각 요청마다 스레드가 생성되거나 기존에 생성된 스레드를 꺼내와 (Thread Pool) 동작한다.
- Servlet 구현체는 싱글톤 패턴을 적용하였기에 하나의 구현체를 통해 동작할 수 있다.
Servlet Flow

- Web Container는 요청을 받으면 Class loader를 통해 Servlet Class를 로드한다. (1번만)
- Servlet Class가 로드되면 인스턴스를 생성한다. ( 1번만 생성하고 싱글톤으로 관리한다.)
- 인스턴스를 생성한 뒤 init()을 호출하여 Servlet을 초기화한다. ( 1번만 초기화한다. )
- 이후 Web Container는 요청이 들어올 때마다 스레드를 통해 Service()를 호출한다.
- Web Container가 종료되기 전 혹은 특정 Servlet 인스턴스에 대한 자원 반납을 진행한다.
- → Destroy() 호출
위에서 나온 init, service, destroy 메서드들은 Web Container가 호출하며, 스레드는 각각의 지역변수 값을 가지고 공유 자원들을 이용한다.
Servlet을 Web Container 동작시 Load 하는 방법?
위에 설명된 Flow를 살펴보면, 요청 시 Servlet Class를 load 한다고 정리되어 있는데 이 방식은 첫 번째 요청이 다른 동일 요청보다 더 많은 시간을 사용한다는 것을 의미한다.
Web.xml의 Mapping Servlet 설정 시 load-on-startup을 이용하면, 서버가 실행될 때 Servlet Class를 Load 할 수 있게 변경할 수 있다.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>post<servlet-name>
<servlet-class>example.servlets.PostServlet</servlet-class>
// 이렇게 작성하고 0 ~ N의 정수를 넘겨주면 그 순서대로 Servlet.Class가 로드된다.
<load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
Servlet URI Mapping
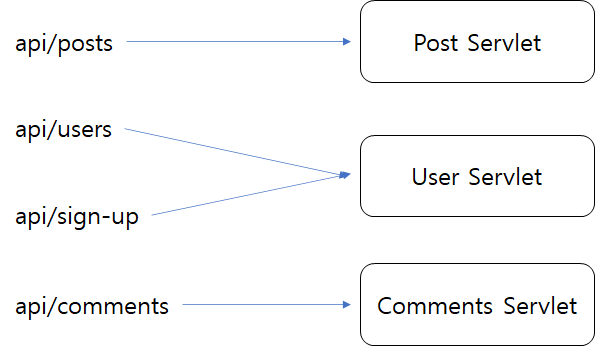
Web Container는 각각의 요청에 대한 URI 정보를 가지고 Servlet 구현체를 매핑하여 준다.
→ 이와 관련된 설정은 Web.xml 에 진행하게 된다.
즉 URL에 따라 여러 Servlet 구현체가 존재하고 Web.xml 파일을 통해 관리된다.
web.xml 예시
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
//context-param....
//listener....
<servlet>
<servlet-name>post</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>example.servlets.PostServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>post</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/posts</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>user</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>example.servlets.UserServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>user</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/users</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>user</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/sign-up</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>comment</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>example.servlets.CommentServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>comment</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/api/comments</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Web Container (Servlet Container)
Servlet의 Life Cycle을 관리하며, Network 통신, Thread 기반의 병렬 처리를 대행한다.
- Servlet 스펙을 구현하고 HTTP 요청을 자바 API로 변환하는 등의 행위를 한다.
- Client의 웹 요청을 해석하여 적정한 Servlet 구현체의 메서드를 ServletRequet, ServletResponse 매개변수와 함께 호출한다.
- Web Server나 WAS에서 동작한다.
- → ( ex) Tomcat : Tomcat은 Web Server의 일반적인 몇몇 기능들을 제공하지 않는다.)
Web Container Flow

- Web.xml 설정 정보를 통해 요청과 Servlet을 Mapping 한다.
- 이 요청에 대한 req, res 객체를 생성한다.
- 생성하였거나, 스레드 풀에서 꺼내온 스레드를 이용하여 서비스 메서드를 호출한다.
- 호출된(HttpServlet) 서비스 메서드는 Servlet 구현체의 서비스 메서드를 호출한다.
- → 해당 메서드에서는 Servlet 응답, 요청 객체를 HttpServlet 응답, 요청으로 Casting 한다.
- 서비스 메서드에서 요청 객체의 메서드 유형(HTTP Method)을 파악하고 해당하는 메서드를 호출한다. (doGet(), doPost()....)
- 호출된 유형별 메서드는 해당 요청을 처리하고 응답 객체에 저장한 뒤 반환한다.
- Servlet Container는 Client에게 응답을 보내고 요청, 응답 객체를 삭제한다.
Servlet Context
하나의 Servlet이 Servlet Container와 통신하기 위해 사용하는 메서드들을 관리하는 인터페이스이며, Web Container에 의해 생성된다. 컨테이너가 객체를 관리하기 위한 인터페이스
- Servlet Container에서 생성되는 Application 단위의 Servlet 요청들을 관리한다. (Tomcat)
- Servlet에 대한 정보 접근을 도와준다. (Servlet API 지원)
- 파일의 MIME 유형 가져오기, 요청 전달, 로그 파일 작성 등에 사용된다.
- web.xml에서 구성 정보를 가져오는 데 사용된다.
<context-param> <param-name>driverName</param-name> <param-value>....XxxDriver</param-value> </context-param> PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); // Context context = getServletConfig().getServletContext(); ServletContext context = getServletContext(); out.println(sc.getInitParameter("driverName"));
Servlet의 구현체들
각각의 구현체들은 GenericServlet이나 HttpServlet을 상속받아 구현한다.
WAS, Servlet Container
- Servlet Interface
- GenericServlet
- HttpServlet 등
Spring Framework
- HttpServletBean
- FrameworkServlet
- DispatcherServlet
GenericServlet?
클라이언트 요청을 처리하는 메서드인 service()를 재정의하여야 하는 일반적인 인터페이스.
HTTP를 제외한 별도의 독립적인 프로토콜을 이용하는 서블릿을 만들 때 사용한다.
public class ExampleServlet extend GenericServlet{
// 재정의
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, SetvletResponse res)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("Service");
}
}
HttpServlet?
HTTP 프로토콜에 대한 요청을 처리하는 Service() 메서드들을 제공하는 구현체이다.
- ServletRequest, Response를 HttpServlet 형식으로 Casting 하는 Service()
- 요청 Method 타입에 따라 별도의 로직을 실행하는 service()가 존재한다.
// 해당 메서드는 요청을 casting하는 service()에서 호출한다.
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 해당 요청의 메서드 값
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
HttpServletBean?
Servlet init()과 관련하여 초기에 설정되는 값들을 Bean 속성으로 매핑하는 확장 클래스이다.
Spring Framework에서 사용되는 모든 Servlet에 대해 적용된다.
// 구성 매개 변수를 매핑한 뒤 초기화를 진행한다.
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
HttpServlet의 기본 동작을 상속받지만, 모든 요청 처리에 대해서 Sub Class에게 위임한다.
(FrameworkServlet, DispatcherServlet은 해당 구현체를 상속받는다.)
FrameworkServlet?
Spring Framework에서 사용되는 Servlet 기능을 위한 구현체이다.
WebApplicationContext를 통해 Servlet 인스턴스가 관리되게끔 지원한다.
해당 구현체로는 doService()를 처리할 수 없으며, 해당 메서드 처리를 위해서는 하위 구현체를 구현하여야 한다. (DispatcherServlet은 해당 메서드를 구현하고 있다.)
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
/**
* Delegate GET requests to processRequest/doService.
*
Will also be invoked by HttpServlet's default implementation of {@code doHead},
* with a {@code NoBodyResponse} that just captures the content length.
* @see #doService
* @see #doHead
*/
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
/**
* Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}.
* @see #doService
*/
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}코드를 보게 되면 doService()는 추상 메서드로, doPost, doGet 등은 별도 처리를 거치고 위임을 하는 형식을 지닌다.
Default Context는 XMLApplicationContext이다.
(HttpServletBean이 xml기반이기 때문일까?)
DispatcherServlet?
Spring MVC는 하나의 Servlet을 통해 요청을 처리하고 매핑하는 형식의 구조를 지닌다.
비즈니스 로직에 대하여서는 Adapter를 통해 Mapping 된 컨트롤러에게 위임하며, 설정 값에 따라 Resolver를 선택하거나 컨버터를 통해 랜더링을 거치고 결과를 반환한다.
'Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring AOP와 요청 인터셉트 개념 (0) | 2021.05.13 |
|---|---|
| 주니어 개발자의 Java, Spring 자료 정리 For Github (1) | 2021.04.29 |
| DBMS 별 Transaction Read Only에 대한 동작 방식 - (0) | 2021.03.12 |
| RESTful API 03. 예제를 더욱더 RESTful하게! - ETag + URI (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| 객체 변환하기. 자바 코드 매핑 vs MapStruct vs ModelMapper? (0) | 2021.03.04 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- URN
- mybatis
- WiredTiger
- RESTful
- AMQP
- transaction
- Url
- Switch
- Request Collapsing
- 근황
- JVM
- java
- cglib
- 커뮤니티 오거나이저
- 회고
- HTTP
- 게으른개발자컨퍼런스
- URI
- RPC
- spring
- JPA
- rabbitmq
- 2025년 회고
- spring AOP
- configuration
- Redis Key
- lambda
- 한국 스프링 사용자 모임
- Optimistic Locking
- JDK Dynamic Proxy
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
